[ad_1]
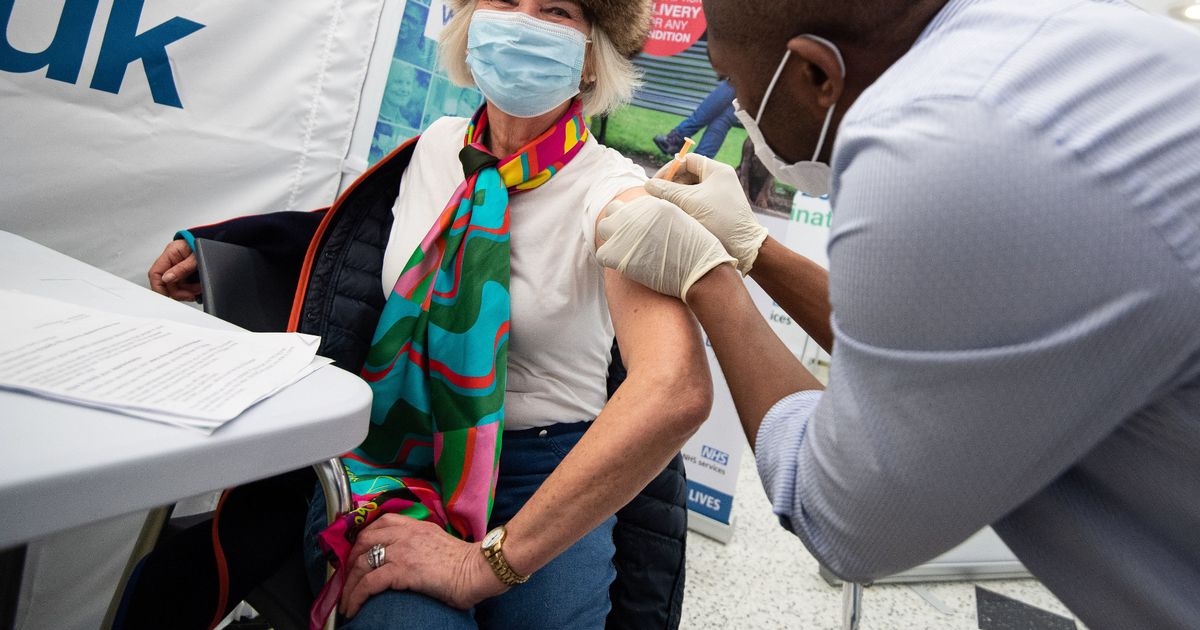
The Oxford-AstraZeneca coronavirus vaccine may reduce transmission by 67%, a study claims.
Scientists say the jab also offers protection of 76% up to 12 weeks after a single dose.
And it rose to 82% after people were given the second dose, according to researchers from the University of Oxford.
The findings were hailed as showing how vaccines are the way out of the pandemic.
The study, on 17,000 people in the UK, South Africa and Brazil, supports the four to 12-week gap between doses many global regulators have recommended.
Before the results, little was known about how effective the Covid-19 vaccines were at preventing transmission of the disease.

(Image: PA)
This is key as by stopping the virus spreading, it means people who have been vaccinated are indirectly protecting others as well.
Researchers said the results show the jab “may have a substantial impact on transmission†by reducing the number of infected people.
For the study, they swabbed participants weekly to test them for Covid.
The UK has made its current priority giving a first dose to as many people as possible, in order to give more Brits some protection.
It means people have to wait around three months for a second ‘booster’ shot instead of three weeks.
Figures show more than 10million doses have now been given in the UK – more than 9.6million first doses and nearly 500,000 second doses.
(Image: PA)
Professor Andrew Pollard, chief investigator of the Oxford Vaccine Trial, said the findings support the “policy recommendation made by the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) for a 12-week prime-boost intervalâ€.
He said the study “reassures us that people are protected from 22 days after a single dose of the vaccineâ€.
The scientists also said the effect of dosing interval on efficacy is pronounced.
They found the vaccine efficacy rose from 54.9% with a dosing gap of less than six weeks, to 82.4% when spaced 12 or more weeks apart.
Health Secretary Matt Hancock welcomed the findings, saying the study was “really encouragingâ€.
He adding that “vaccines are the way out of the pandemic”.
The paper is currently under review at The Lancet journal.
[ad_2]
Source link