[ad_1]
Chinese billionaires Jack Ma and Joe Tsai have pledged chunks of their combined $35bn stake in ecommerce group Alibaba in exchange for significant loans from investment banks, company documents show.
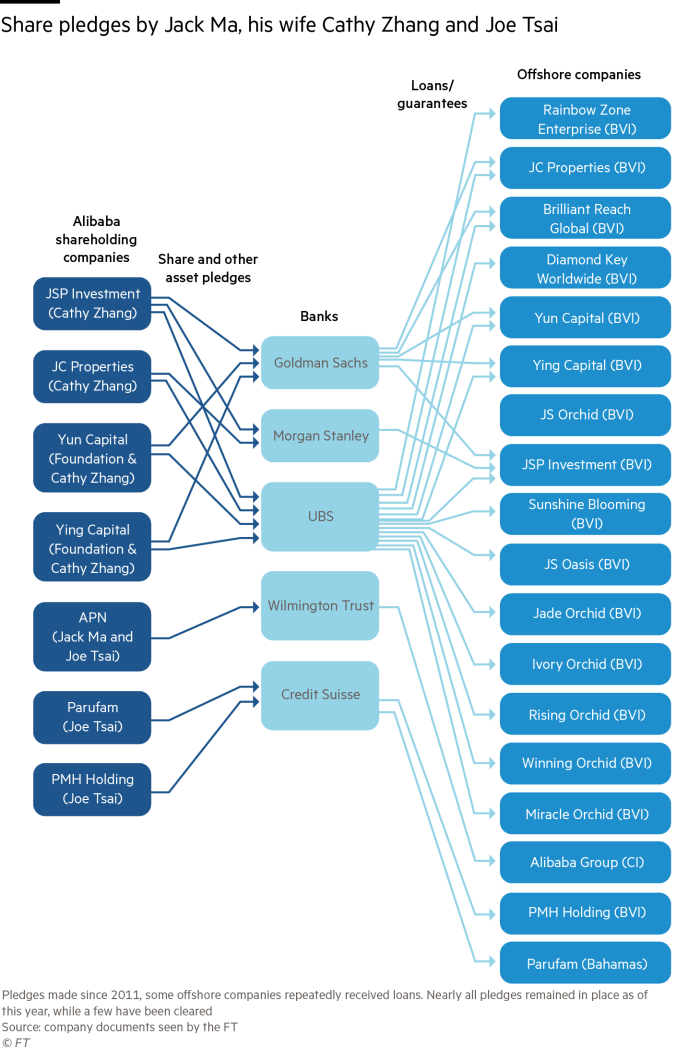
The share pledges, made to banks including UBS, Credit Suisse, Goldman Sachs and others, were undertaken by offshore companies controlling more than half of the two billionaires’ stakes in Alibaba, which totalled 5.8 per cent as of December. In share pledging, banks accept stock as collateral for loans but the borrower retains ownership of the shares.
The amounts of most of the share pledges were not disclosed in the documents but the pair have repeatedly turned to borrowing against their stock since Alibaba listed in the US in 2014, the documents seen by the Financial Times show.Â
Ma and Tsai, Alibaba’s two largest individual shareholders, have used the loans to unlock vast personal fortunes tied up in the group’s shares.
Global banks have extended a wide variety of credit to Ma and Tsai. Tsai’s Gulfstream 650ER private jet is mortgaged to Credit Suisse. The Swiss bank, which brought Alibaba to market, also extended credit during the IPO run-up to an offshore shell company later linked to Ma’s purchase of a lavish house in Hong Kong’s elite Peak district and a new plane the same model as Tsai’s.Â
Share pledging carries risks and is limited by most US companies. Any forced selling of executives’ pledged stock can exacerbate the fall of a company’s share price. This can be precipitated by margin calls, when borrowers must pay back loans from brokers or forfeit stock.
Credit Suisse, Nomura, Morgan Stanley, UBS, Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group and Mizuho lost more than $10bn this year when they were forced to liquidate positions in US-listed companies held by family office Archegos after it failed to meet margin calls.
Alibaba said Ma “and his affiliates†currently did not have any loans outstanding collateralised by Alibaba shares while Tsai’s loans outstanding backed by shares were “easily manageable†with “prudent loan-to-value ratios to provide [a] substantial cushion against triggering a margin callâ€.
The company said pledging shares for loans was part of “ordinary financial planning to provide liquidity and diversification without having to sell shares in Alibabaâ€.
Ma stepped down as executive chair of Alibaba in 2019 while Tsai remains executive vice-chair.

Web of offshore companies
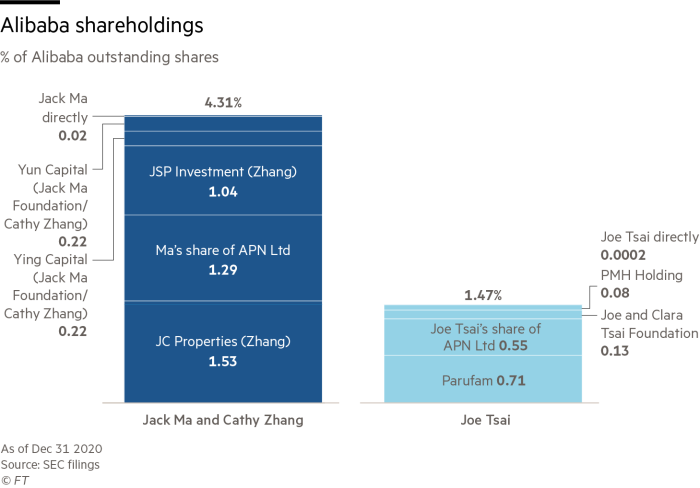
Ma and Tsai’s interests in Alibaba are held mainly through five offshore companies: JC Properties, JSP Investment, Parufam, PMH Holding and APN Ltd.Â
APN has made the biggest known single pledge of Alibaba stock at 400m shares. But rather than in exchange for a loan, this was part of guarantees made to Japan’s SoftBank and Yahoo after Ma carved out Alibaba’s payments unit Alipay — now part of his fintech Ant Group — from the ecommerce company.
Ma’s wife Cathy Ying Zhang, who has taken Singaporean citizenship, has been instrumental in his dealings. Records show that two offshore holding companies of which Zhang is the sole director, JSP Investment and JC Properties, hold 60 per cent of the couple’s Alibaba stake.
Altogether, Zhang’s two holding companies for Alibaba shares have made more than a dozen asset pledges to investment banks for loans extended to a web of offshore companies.Â
In addition, Zhang is the sole shareholder of a Hong Kong company Ma used to buy a château and vineyards in France and has power over the well-endowed Jack Ma Philanthropic Foundation, business records show. She has also signed off on cheap loans from Goldman Sachs to Enbao Asset Management, Ma’s family office.
In one deal, an investment in a Chinese online real estate platform in 2015 that was orchestrated by Enbao, Ma used two offshore holding companies to contribute $20m. One was BVI-based Rainbow Zone Enterprise, which contributed $10m while at the same time taking a loan from Swiss bank UBS that was collateralised against unspecified securities pledged to the bank by JSP Investment.Â
On one day in 2019, the couple set up three shell companies, Miracle Orchid Investment, Rising Orchid Investment and Winning Orchid Investment. Three months later they received loans backed by JSP Investment’s assets.
The records seen by the FT made clear that Alibaba’s American Depositary Shares had been pledged for loans from Morgan Stanley and Credit Suisse, while Goldman referred to pledged American Depositary Shares, and UBS reported pledged “securities†and other assets.
BVI-based Diamond Key Worldwide, another company Zhang controls, has received four separate loans from UBS. Last year, the company’s Chinese subsidiary bought a Rmb35m ($5.4m) piece of land in Hangzhou, where Alibaba is based, to develop for educational purposes.
Unlocking liquidity without alarming markets
Bankers say stock pledges are a common method for Chinese executives to raise cash without losing control of their companies or sending negative signals to the market by selling their shares.
“It’s a really good business for banks, it feeds a lot of people,†said one former banker. “These founders are asset rich but cash poor.â€
American executives such as Tesla co-founder Elon Musk have also pledged shares in their companies for loans. But as a US company, Tesla has to disclose the pledges to shareholders under Securities and Exchange Commission rules.
But under looser US disclosure requirements for “foreign private issuersâ€, a category that includes nearly every Chinese tech group listed in the US including Alibaba, Ma and Tsai have no obligation to reveal their share pledges.
The documents show many of the share and other asset pledges of Tsai, Ma and his wife Zhang remained in place as of January, even as they have started to sell down their Alibaba shares.Â
Ma and his wife have cashed out an estimated $11.4bn of stock since Alibaba floated in New York, with the majority sold starting in 2017. His charitable foundation has sold another $4.1bn. Tsai has sold an estimated $5.4bn.Â
Alibaba said Ma and Tsai had owned “the company’s stock for 22 years and continue to have significant holdings in Alibaba, which make up the majority of their wealthâ€.
A former English teacher, Jack Ma is one of China’s best-known entrepreneurs, co-founding Alibaba with Tsai in 1999 before building a fortune estimated by Bloomberg at $49.9bn.
Late last year, however, he largely disappeared from public view after Beijing began a crackdown on Ant Group, the fintech Ma carved out of Alibaba in 2011.Â
Credit Suisse, Morgan Stanley, Goldman Sachs and UBS declined to comment.
Additional reporting by Joe Leahy in Hong Kong
[ad_2]
Source link





